
Sonication to nanoparticles, nano emulsions,nano crystals, liposomes and wax emulsions
Sonication has numerous effects, both chemical and physical. The chemical effects of ultrasound are concerned with understanding the effect of sonic waves on chemical systems, this is called sonochemistry.The chemical effects of ultrasound do not come from a direct interaction with molecular species. Studies have shown that no direct coupling of the acoustic field with chemical species on a molecular level can account for sonochemistry or sonoluminescence. Instead, sonochemistry arises from acoustic cavitation: the formation, growth, and implosive collapse of bubbles in a liquid.
Sonication can be used for the production of nanoparticles, such as nanoemulsions,nanocrystals, liposomes and wax emulsions, as well as for wastewater purification, degassing, extraction of plant oil, extraction of anthocyanins and antioxidants,production of biofuels, crude oil desulphurization, cell disruption, polymer and epoxy processing, adhesive thinning, and many other processes. It is applied in pharmaceutical, cosmetic, water, food, ink, paint, coating, wood treatment, metalworking, nanocomposite, pesticide, fuel, wood product and many other industries.
Sonication can be used to speed dissolution, by breaking intermolecular interactions. It is especially useful when it is not possible to stir the sample, as with NMR tubes. It may also be used to provide the energy for certain chemical reactions to proceed. Sonication can be used to remove dissolved gases from liquids (degassing) by sonicating the liquid while it is under a vacuum. This is an alternative to the freeze-pump-thaw and sparging methods.
In biological applications, sonication may be sufficient to disrupt or deactivate a biological material. For example, sonication is often used to disrupt cell membranes and release cellular contents. This process is called sonoporation. Sonication is also used to fragment molecules of DNA, in which the DNA subjected to brief periods of sonication is sheared into smaller fragments.
Sonication is commonly used in nanotechnology for evenly dispersing nanoparticles in liquids.
Sonication can also be used to initiate crystallisation processes and even control polymorphic crystallisations. It is used to intervene in anti-solvent precipitations (crystallisation) to aid mixing and isolate small crystals.
Sonication is the mechanism used in ultrasonic cleaning—loosening particles adhering to surfaces. In addition to laboratory science applications, sonicating baths have applications including cleaning objects such as spectacles and jewelry.
Sonication is also used to extract microfossils from rock.
Sonication can also refer to buzz pollination – the process that bees use to shake pollen from flowers by vibrating their wing muscles.
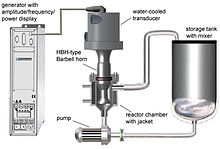
Substantial intensity of ultrasound and high ultrasonic vibration amplitudes are required for many processing applications, such as nano-crystallization, nano-emulsification, deagglomeration, extractio
© Copyright: 2024 Hangzhou Altrasonic Technology Co.,Ltd All Rights Reserved

IPv6 network supported
Scan to WhatsApp
